Hydrotherapy Treadmill Benefits for MS
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis and Mobility Challenges
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune condition that disrupts communication between the brain and the body, often leading to muscle weakness, fatigue, and impaired coordination. For many individuals, mobility challenges become a daily struggle, limiting independence and quality of life. Traditional exercise can feel daunting due to the risk of overheating or overexertion, which may exacerbate symptoms. Hydrotherapy, particularly using underwater treadmills, has emerged as a promising solution. By leveraging the properties of water—such as buoyancy, resistance, and temperature control—this therapy offers a safer environment for MS patients to rebuild strength and confidence.

What Is a Hydrotherapy Treadmill?
A hydrotherapy treadmill is a specialized device submerged in a pool, allowing users to walk or jog against adjustable water resistance. Unlike land-based treadmills, the water’s buoyancy reduces joint impact, while viscosity provides natural resistance to strengthen muscles. The temperature-controlled environment (typically around 88–92°F) helps regulate body heat, critical for MS patients sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Many systems also include harnesses or rails for stability, accommodating varying levels of mobility. This combination of features creates a low-risk, high-reward exercise modality tailored to the unique needs of those with neurological conditions.
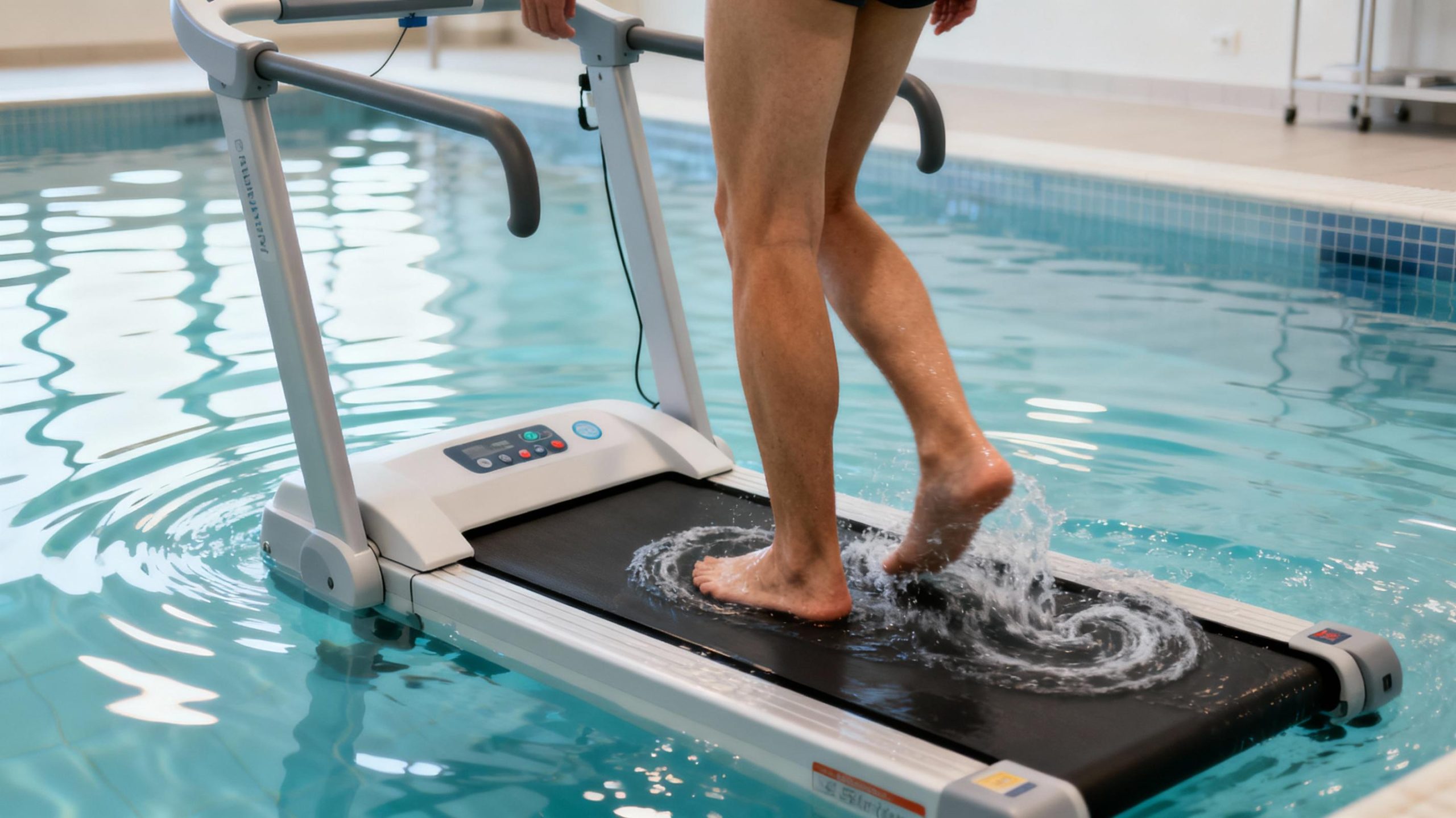

Reducing Joint Stress Through Buoyancy
One of the most significant advantages of hydrotherapy treadmills for MS patients is buoyancy. Water supports up to 90% of body weight, alleviating pressure on joints, tendons, and ligaments. This is especially beneficial for individuals with spasticity or balance issues, as it minimizes fall risks and allows smoother movements. Unlike land exercises, which may strain weakened muscles, aquatic buoyancy enables longer, pain-free sessions. Over time, this can improve gait patterns and reduce reliance on assistive devices, fostering greater independence in daily activities.
Enhancing Muscle Strength and Coordination
Water’s natural resistance provides a unique strength-training medium. Every movement on a hydrotherapy treadmill engages muscles more comprehensively than air-based exercises, promoting endurance and motor control. For MS patients, this can counteract muscle atrophy and spasticity. The treadmill’s adjustable speed and water depth allow personalized progression, ensuring workouts remain challenging yet achievable. Studies show consistent hydrotherapy can improve lower-body strength, coordination, and overall functional mobility—key factors in managing MS-related disability.
Improving Balance and Reducing Fall Risks
Balance impairment is a common MS symptom, increasing fall risks and limiting mobility. Hydrotherapy treadmills address this by combining buoyancy with controlled instability. The water’s gentle resistance forces users to engage core stabilizer muscles, enhancing proprioception and postural control. Over time, patients often report improved confidence in navigating uneven surfaces or crowded spaces. Additionally, the secure pool environment allows safe experimentation with challenging movements, which would be risky on land.
Managing Spasticity and Pain
Hydrotherapy’s warm water can relax stiff muscles, alleviating MS-related spasticity. The heat dilates blood vessels, enhancing circulation and reducing muscle tightness. Meanwhile, the treadmill’s rhythmic movements promote range of motion without overstraining joints. Many patients find this combination more effective than medication alone for pain management. Regular sessions may also decrease reliance on antispasmodic drugs, minimizing side effects like dizziness or fatigue.
Boosting Cardiovascular Health Safely
Cardiovascular exercise is vital for MS patients but challenging to achieve safely. Hydrotherapy treadmills enable heart-healthy workouts without overheating. Water’s cooling properties help regulate body temperature, while resistance ensures heart rates stay elevated. Improved cardiovascular fitness can combat MS-related fatigue and enhance overall stamina, making daily tasks feel less exhausting.
Mental Health Benefits of Aquatic Exercise
Beyond physical gains, hydrotherapy fosters mental well-being. The weightlessness of water can feel liberating for those who face mobility restrictions on land. Exercise-induced endorphins alleviate depression and anxiety, common MS comorbidities. Group sessions also offer social interaction, reducing feelings of isolation. Many patients describe hydrotherapy as a meditative experience, where the water’s rhythm provides emotional calm.
Tailoring Hydrotherapy for Different MS Stages
Hydrotherapy programs can be adapted for varying MS severities. Early-stage patients might focus on intense resistance training, while those with advanced disability can work on gentle range-of-motion exercises. Therapists adjust water depth, speed, and session duration to match individual capabilities. This flexibility ensures long-term engagement, critical for slowing disease progression and maintaining functional abilities.
Getting Started: Choosing the Right Program
When exploring hydrotherapy, consult a neurologist or physiotherapist familiar with MS. Look for facilities with MS-trained staff and ADA-compliant pools. Initial sessions should focus on acclimating to the environment and establishing baseline capabilities. Over time, gradually increase intensity while monitoring symptom responses. Many centers offer trial sessions, allowing patients to experience benefits firsthand before committing.