Virtual Reality Balance Training Suites
The Evolution of Balance Training: Enter Virtual Reality
Balance training has long been a cornerstone of physical rehabilitation, athletic conditioning, and general fitness. Traditional methods, from wobble boards to foam pads, have focused on challenging the body's proprioceptive system. Now, virtual reality (VR) is revolutionizing this space by merging immersive technology with neuroscience-driven exercises. VR balance training suites offer dynamic, adaptive environments that replicate real-world challenges while tracking progress with precision. This fusion of tech and physiology isn’t just about novelty—it’s a leap toward personalized, data-driven wellness.

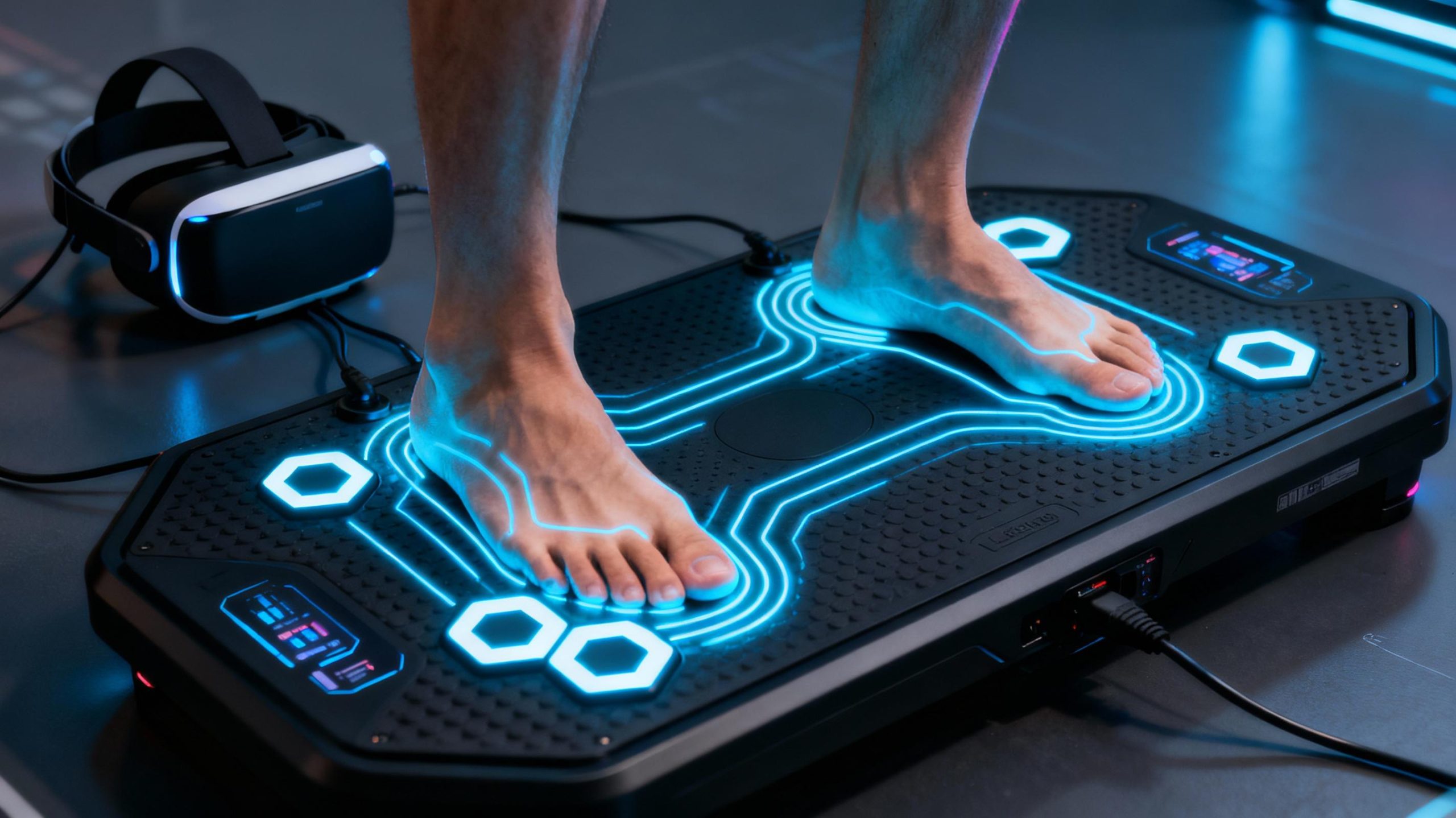
How VR Balance Systems Work: Sensors, Software, and Synergy
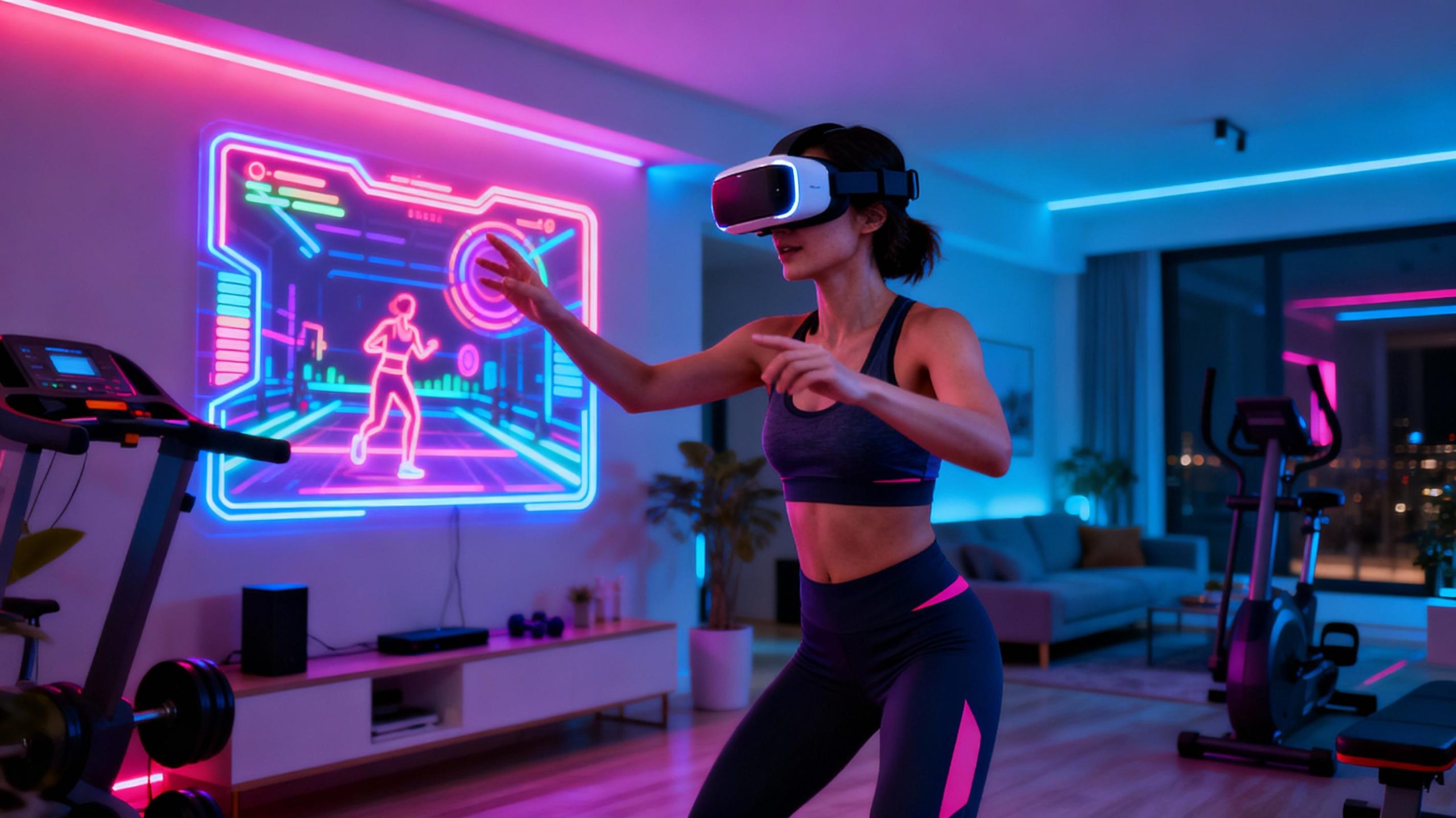
At the core of VR balance training lies a trifecta of hardware, software, and biomechanics. Motion sensors embedded in floors or wearable devices track shifts in weight distribution, while VR headsets overlay responsive environments. Advanced algorithms adjust difficulty in real time—for example, narrowing a virtual balance beam if a user excels—or introducing gusts of "wind" to destabilize posture. Haptic feedback vests or gloves add tactile cues, simulating external forces. This ecosystem turns static exercises into interactive scenarios, from crossing icy streams to navigating storm-tossed ships.

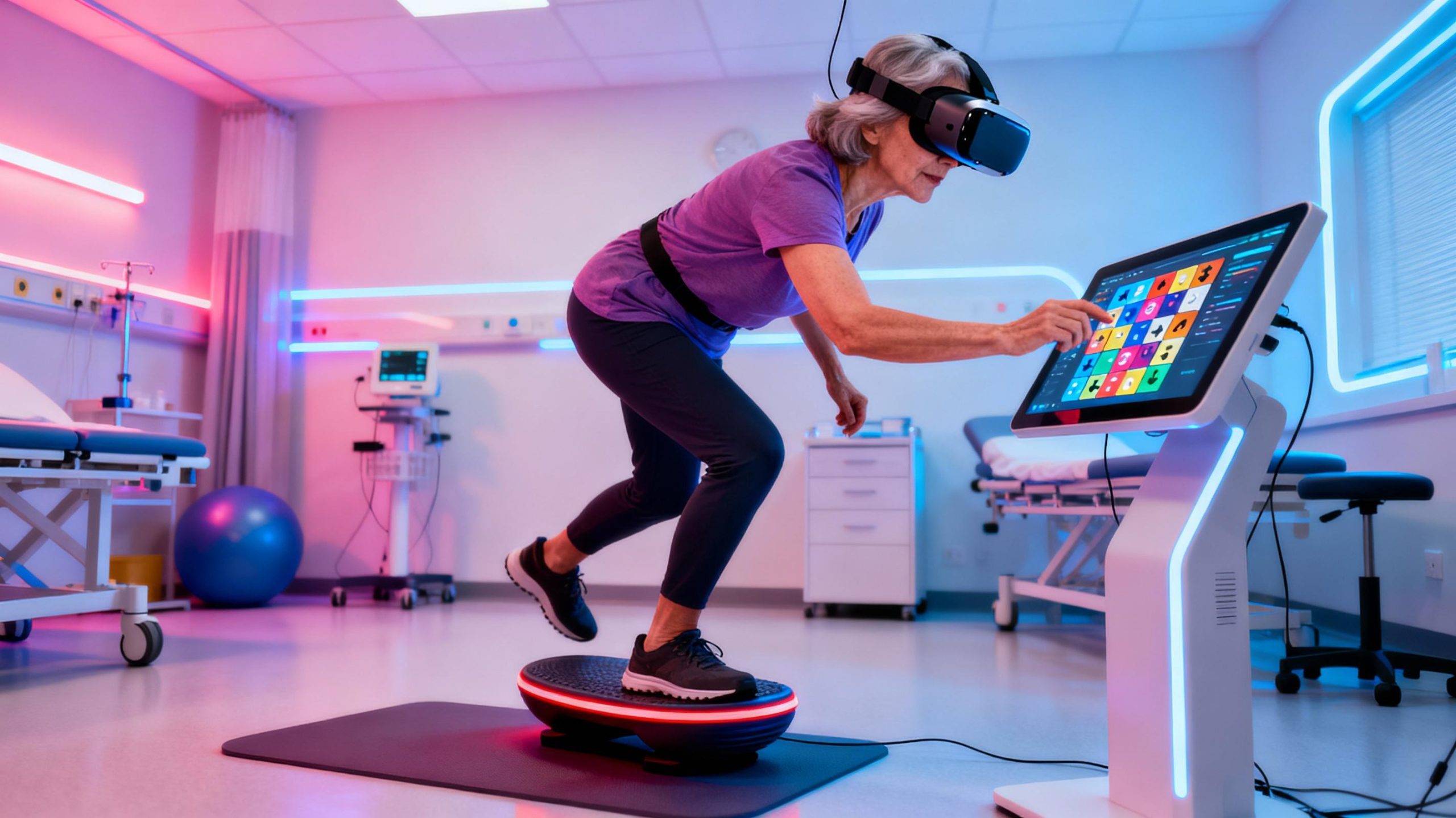
Rehabilitation Redefined: Stroke Recovery and Beyond
Clinics are adopting VR balance programs for patients recovering from strokes, spinal injuries, or vestibular disorders. Unlike repetitive clinical drills, VR tasks like catching virtual butterflies or balancing on a swaying bridge engage cognitive-motor coordination. Studies show such immersion accelerates neuroplasticity by 20-30% compared to conventional methods. Therapists praise the instant feedback: heatmaps highlighting asymmetrical weight bearing or response-time metrics guide targeted interventions. For Parkinson’s patients, VR’s gamified tasks improve freezing-of-gait episodes by training the brain to adapt mid-movement.
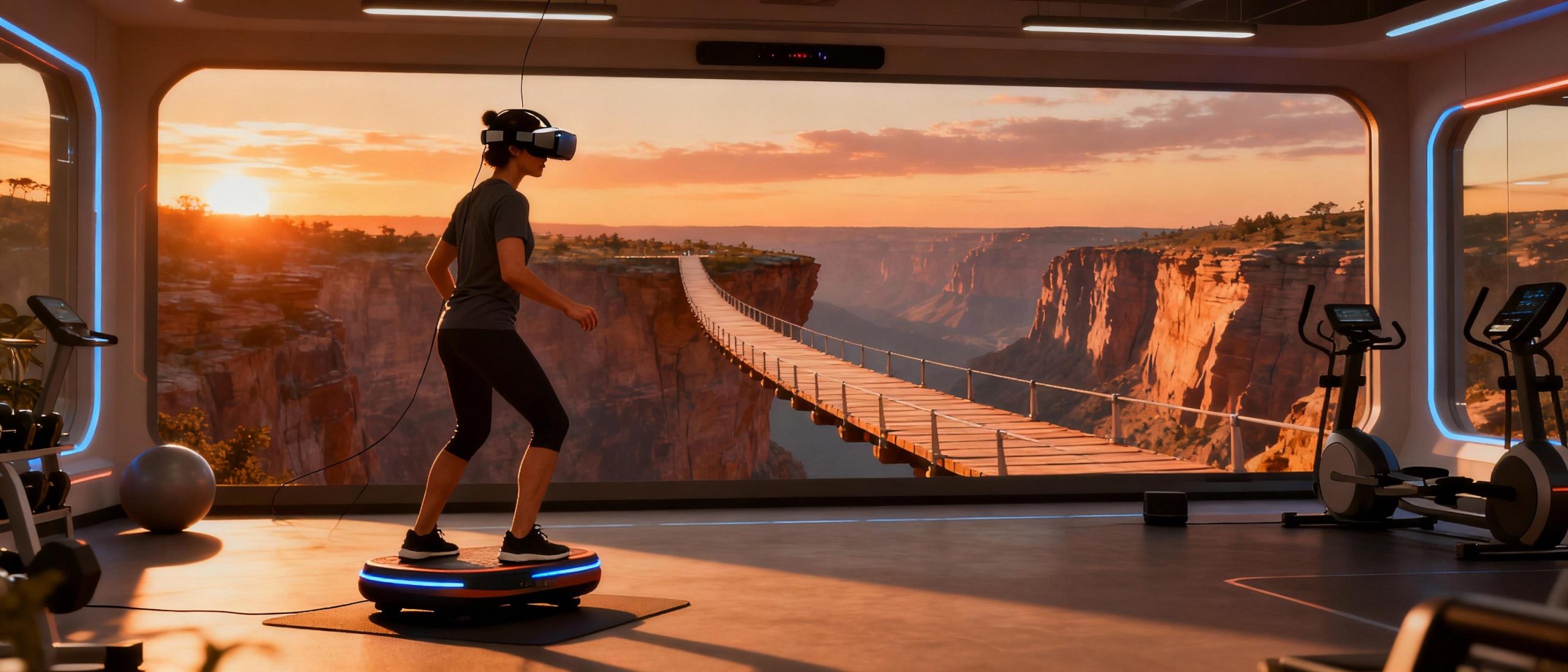
From Gym Floors to Pro Sports: Athletes Embrace VR Conditioning
Elite athletes now use VR balance suites to simulate high-pressure environments—think surfers preparing for choppy waves or gymnasts perfecting landings. The Golden State Warriors’ training facility includes VR modules that mimic crowd noise and visual distractions during free-throw practice. Skiers use tilting platforms paired with VR slopes to drill muscle memory without weather constraints. These systems also reduce injury risk: by identifying subtle imbalances during jumps or pivots, coaches tailor strengthening routines preemptively.
Accessibility and Adaptation: Making Balance Training Inclusive
VR balance training isn’t limited to high-end clinics or pro teams. Affordable standalone headsets like the Meta Quest 3 now support consumer-grade apps. Seniors can practice fall prevention via serene Tai Chi simulations, while children with ADHD engage with ADHD-specific reactivity games. Researchers at MIT even developed a VR system for wheelchair users, using upper-body motions to "steer" through obstacle courses. By adapting difficulty levels and providing anonymity, VR reduces the stigma often felt in group rehab classes.
The Future of Balance Training: AI, Wearables, and Beyond
Emerging technologies promise even smarter systems. AI-driven avatars will coach users through missteps, while EEG headsets could detect neural fatigue before physical strain. Companies like Nintendo are exploring hybrid AR/VR balance games for home use. Meanwhile, military researchers test VR suites to reduce motion sickness in pilots. As haptic suits become lighter and 5G enables real-time remote coaching, VR balance training may soon be as commonplace as yoga mats—a silent revolution beneath the headset’s glow.